Go Direct® Respiration Belt
By Edwin P. Christmann
Posted on 2018-07-05
Introduction
The Go Direct Respiration Belt measures human respiration rate. While using the Go Direct Respiration Belt, you can measure human breathing patterns with a wireless Bluetooth connection or by plugging-in the device with a USB cord. It works with a sensor and an adjustable nylon strap that goes around the chest to measure respiration effort and respiration rate. So that belt tension can be optimized, an LED indicator provides feedback.
First, if using the Bluetooth, the device will need to be charged, which takes approximately two hours. Respiration rate and exerted force are reported with a free “Graphical Analysis™ 4 app,” which simplifies comparisons between subjects during experiments. The “app” can be downloaded onto a computer or a smart phone.
What’s included:
• Go Direct Respiration Belt
• Micro USB cable


While using the device, the user can observe how respiration rate changes. For example, a student can examine the effect of a particular exercise on respiration effort, which is the force exerted by the chest during respiration changes after exercise or breath holding. Another nice feature is the built-in pedometer, which measure steps and step-rate during experimentation.
To use the Go Direct Respiration Belt, it needs to placed around the subject’s chest or abdomen. Another nice feature of the device is that the sensor does not need to rest directly on the skin in that it can be worn over clothing using a strap and clips (this is included). Subsequently, once the belt is secure, make sure that sensor box is positioned just below the sternum of the subject.
Undoubtedly, the possibilities for Vernier Respiration Belt are unlimited. Nonetheless, our approach to using it included three subjects (all college athletes) doing different exercises. In the example shown below, the subjects all did a different exercise, showing results with how endurance and force applied changes over time during the specified exercise.
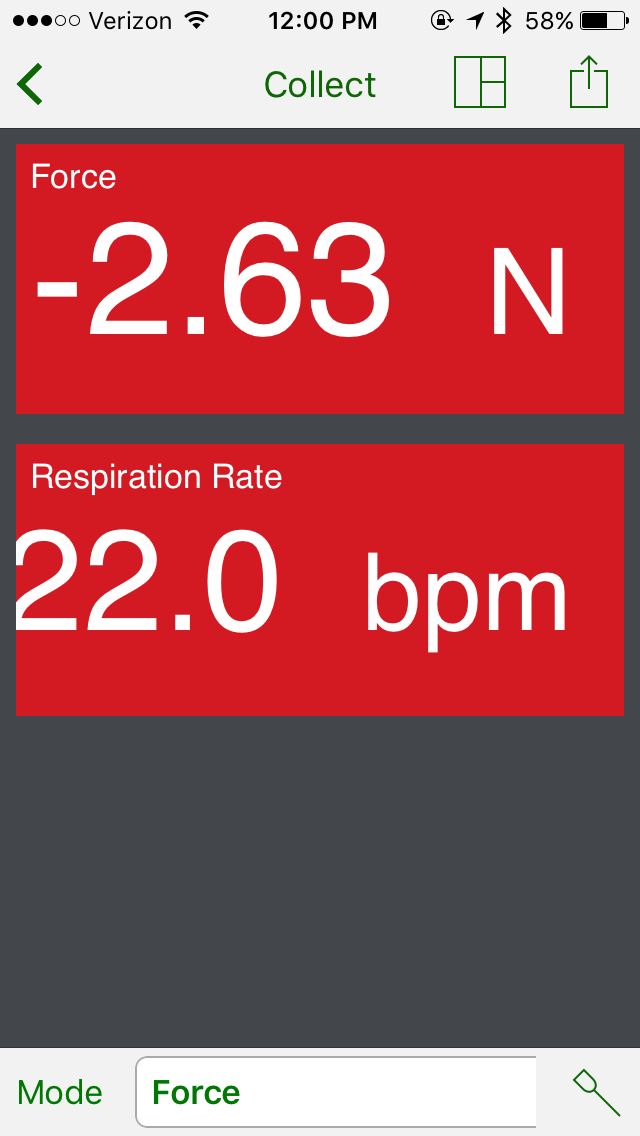
Example 1: Exercise- Boxing
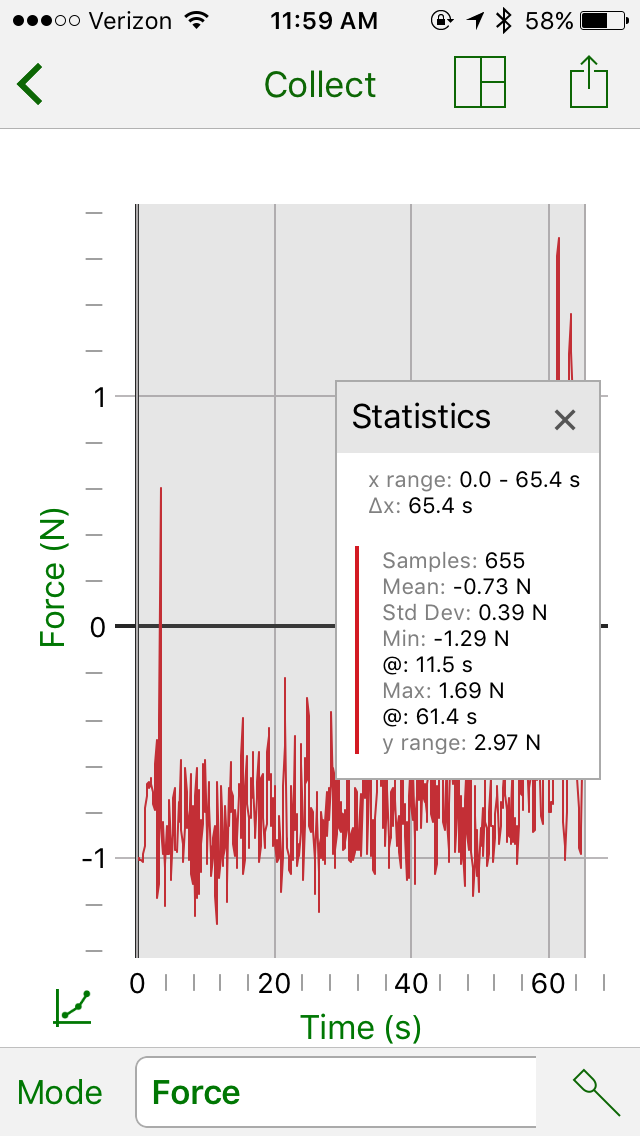
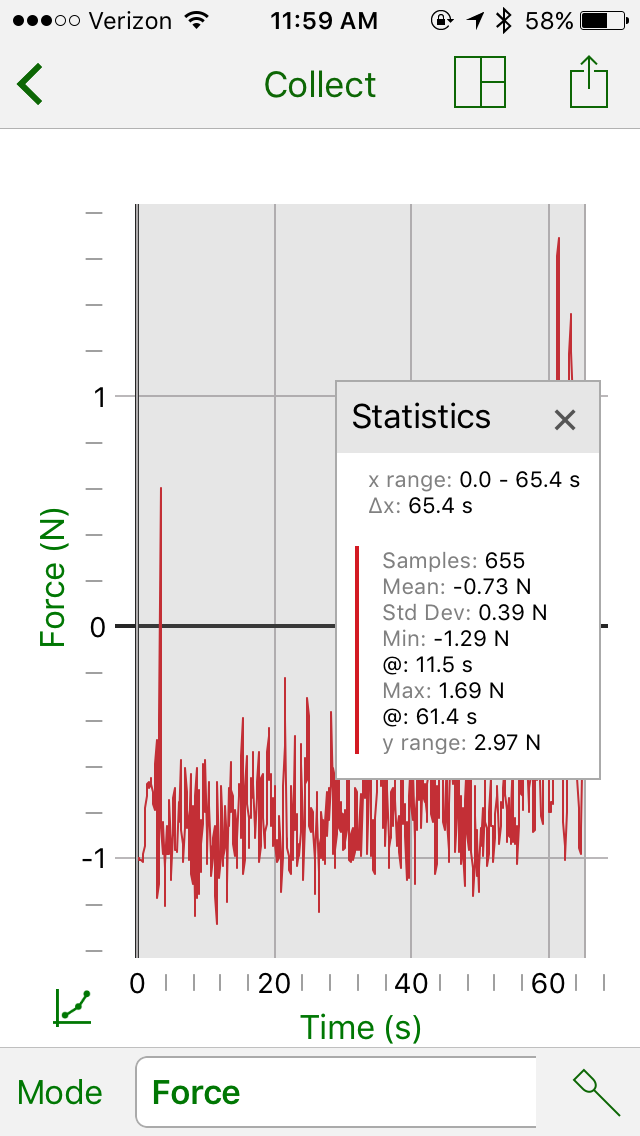
Example 2: Exercise- Jump roping

Example 3: Exercise- Bench press
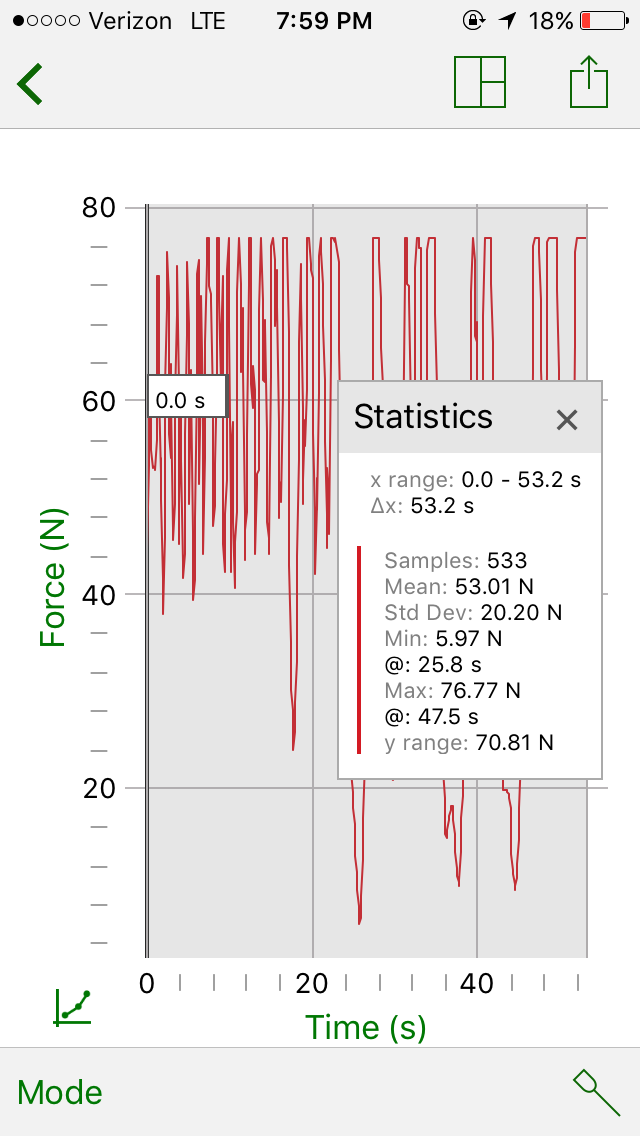
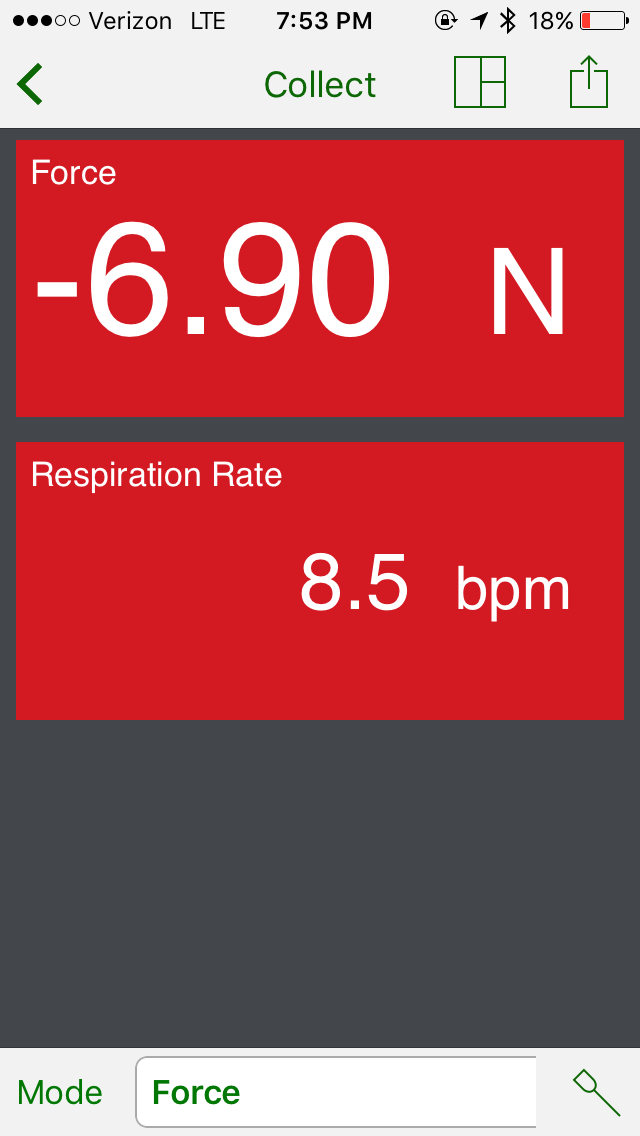
Three different exercises were completed and we recorded the data on a smartphone using the Graphical Analysis™ 4 app. The “app” creates a graph and chart and also shows the force exerted by each subject. The “app” can also show the Respiration rate in the form of BPM, which stands for breaths per minute; showing how many breaths the person is taking per minute during the exercise.
The normal respiration rate for an adult at rest is 12-20 breaths per minute. However, as our results show, the different exercises result in different breaths per minute and different forces exerted.
This product is an excellent tool to compare variation of respiration rates of different subjects during a variety of physical activities. Undoubtedly, the Go Direct Respiration Belt is a great tool to get students physically active in the high school or college classroom!
Summary
After reviewing the Go Direct Respiration Belt, we found that its user-friendly data collection capabilities have many practical uses both within and outside of the classroom. Moreover, the included rechargeable battery is reliable and offers long battery life for experiments.
The Go Direct Respiration Belt is reasonably priced and connects direct to mobile devices. Without doubt, we found it to be a great tool for science and mathematics students to become active and motivated learners. Hence, the Go Direct Respiration Belt is highly recommended for classroom use!
Cost: $99.00
Edwin P. Christmann is a professor and chairman of the secondary education department and graduate coordinator of the mathematics and science teaching program at Slippery Rock University in Slippery Rock, Pennsylvania. Caitlin Baxter is a graduate student in the mathematics and science teaching program at Slippery Rock University in Slippery Rock, Pennsylvania.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this blog post are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official position of the National Science Teaching Association (NSTA).


